FS08: Synthetic Aperture Radar
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is a remote sensing technique typically used from satellites (e.g. Sentinel 1) to provide vegetation, biomass, moisture assessments and mapping of landscapes. The technological adaption for use working with UAV drones allows a higher spatial resolution along with greater level of canopy and soil penetration which supports a much richer assessment of land condition with outcomes that include DTM/DSM/CHM, biomass, vegetation profile, soil moisture, soil types and even shallow buried objects. No one else in the UK has commercial access to this technology.
Background
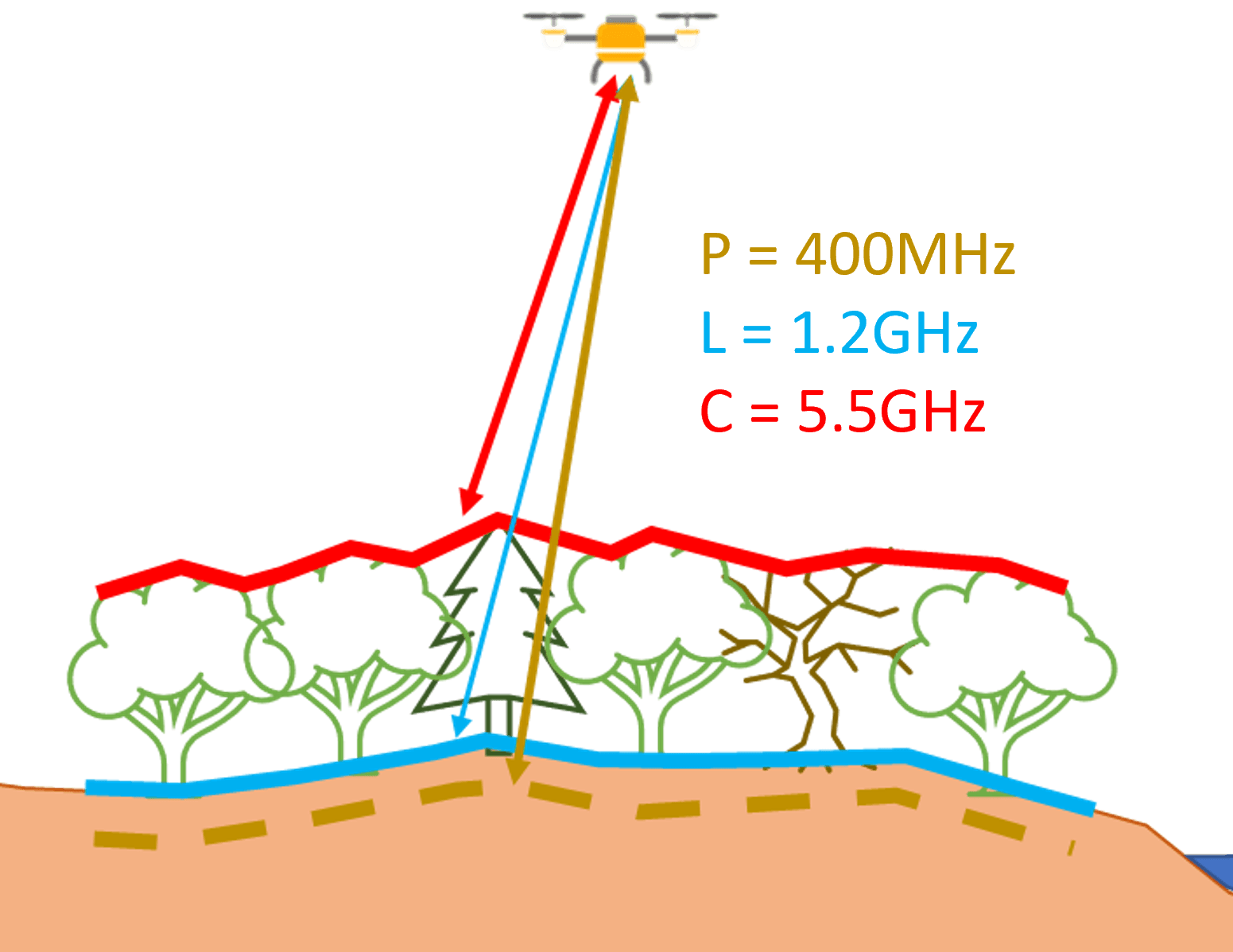
UAV SAR is a unique and emerging technology with significant application. Electromagnetic signals are pulsed and received at high frequency rates from a UAV (or crewed craft). The application of multiple bands of EM spectrum at different wavelengths allows different levels of penetration. The application of different flight modes (height, angle and orientation) allows a range of focus points. The outcomes provide us with rich and complex data but with careful processing can give us unique insights. Modelling and the use of machine learning processes can provide soil and vegetation moisture profiling, biomass, land deformation and assessment of buried objects/voids.
SAR Applications
UAV SAR can be applied in a range of possible use cases, particularly to assess and monitor climate change impacts. These include:
Moisture - Profiling moisture within soils and in vegetation can support agriculture, forest management, wildfire predictions, drought assessment, irrigation optimisation, flood risk, catchment management, drainage and/or slope stability assessment.
Biomass - Profiling of structural features from SAR can provide detailed accounts of biomass to support agriculture and forestry optimisation, carbon assessment and vegetation management for infrastructure.
Deformation - SAR can provide very small variations in ground movement and can be applied over large areas to support applications in mining, slope stability and dam failures.
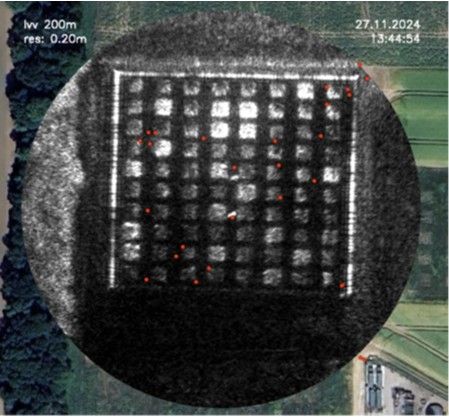
Shallow Voids/ Buried Objects - SAR bands can penetrate into the ground the extent of which is subject to the properties of the soil and any groundwater. This in itself can provide further insight. The technology could be used to identify burrowing animals, tunnels, pipework or archaeological features. This could be suitable for a range of development and infrastructure projects.
The application of one of these outcomes would in itself be exceptionally useful, but having the ability to do all of those from the survey data is very unique.
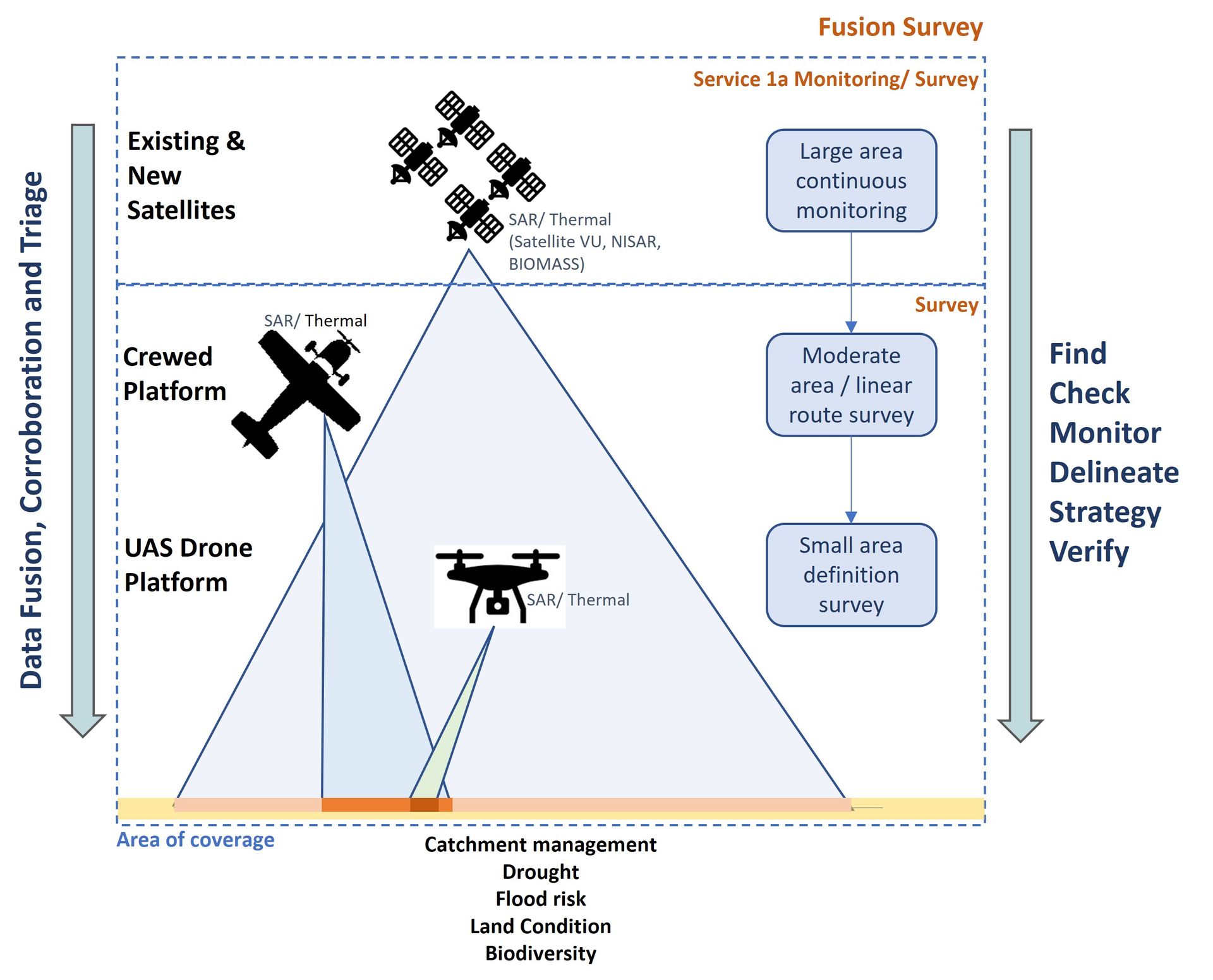
Survey Processes
SAR can be applied with UAV and with crewed craft. UAV processes allow greater level of mission control which are optimised for the data application. Typical missions would include linear and/or helical flights at different heights and tracks. The radar sensors operate at an angle meaning that a target site need not be overflown.
Satellite SAR
Satellite SAR is well established and provides good coverage albeit with limited EM bands and low resolution. Nonetheless, there are commercial satellites with greater capability and increased resolution along with a proposed string a new satellite constellations which will offer even greater insights and most importantly a constant cycle of coverage providing ideal monitoring solutions for larger site areas.
Surveyar have been developing data fusion techniques, where the drone based SAR is used to 'calibrate' the satellite SAR via machine learning processes to increase the resolution and survey outcomes for specific use cases. Further, we are also developing triage solutions which use satellite based data to prioritise areas for aerial survey at higher resolution for 'areas of interest'.
Surveying Examples
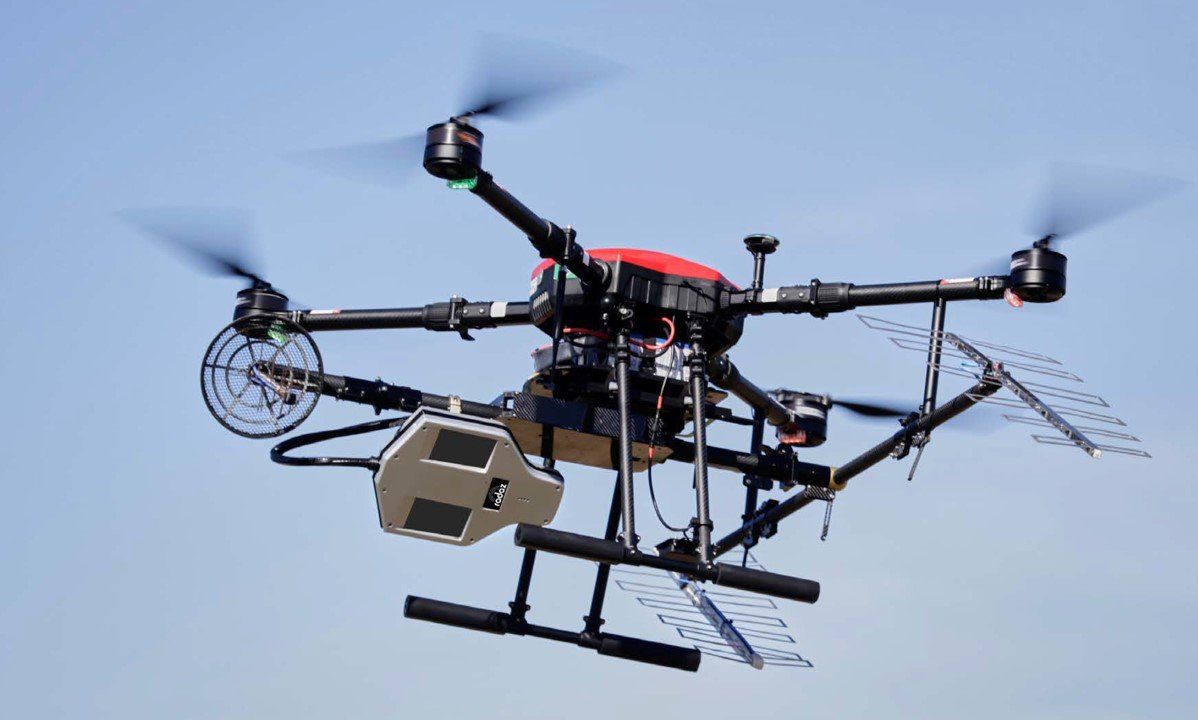

Image of Multiband Radar SAR on Rotary Drone
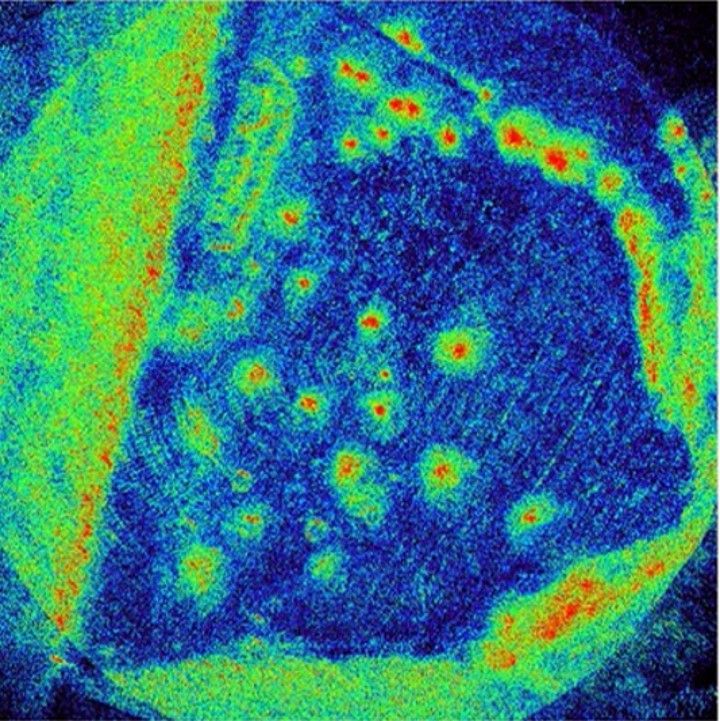
Soil Moisture: Assessment of soil moisture in agri and forest areas.
Research of multiband SAR for soil and vegetation moisture and biomass with Cranfield and for Aberystwyth
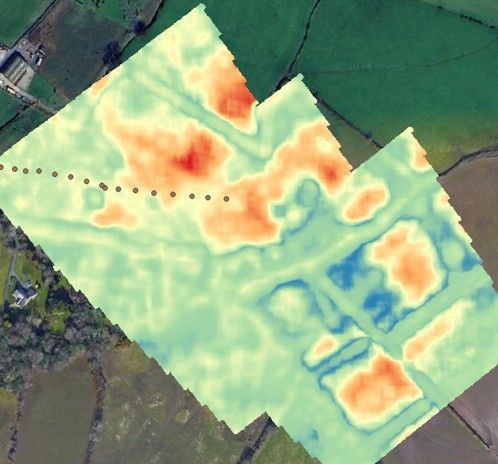

Research using UAV SAR for moisture with Cranfield
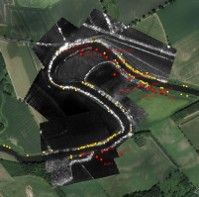
Research of UAV SAR for identification of underground beaver burrows with NatureScot
Read Also
