BS05: Volumetric
Drones with lidar sensor technology can provide full coverage, penetrate vegetation and survey vertical surfaces, providing a revolution in the assessment of volume and monitoring changes in volume.
Definition
Remote environmental survey using photogrammetry and lidar can be used to calculate the volume of specific land-based features or the volume of change. Traditional methods of survey for determining volume and volume change are based on land surveying using GPS. The advent of accurate and reliable drone platforms coupled with higher resolution sensors (photography and lidar etc) with more advanced GPS now offer an alternate and potentially more efficient mechanism for calculating volumes.
Method Differences
There are benefits and disadvantages in both types of survey and hence both should be retained within your armoury for volumetric based surveys to ensure that you use the best tool and approach for the need and use case that you have.
The following table summarises the key differences in each approach.

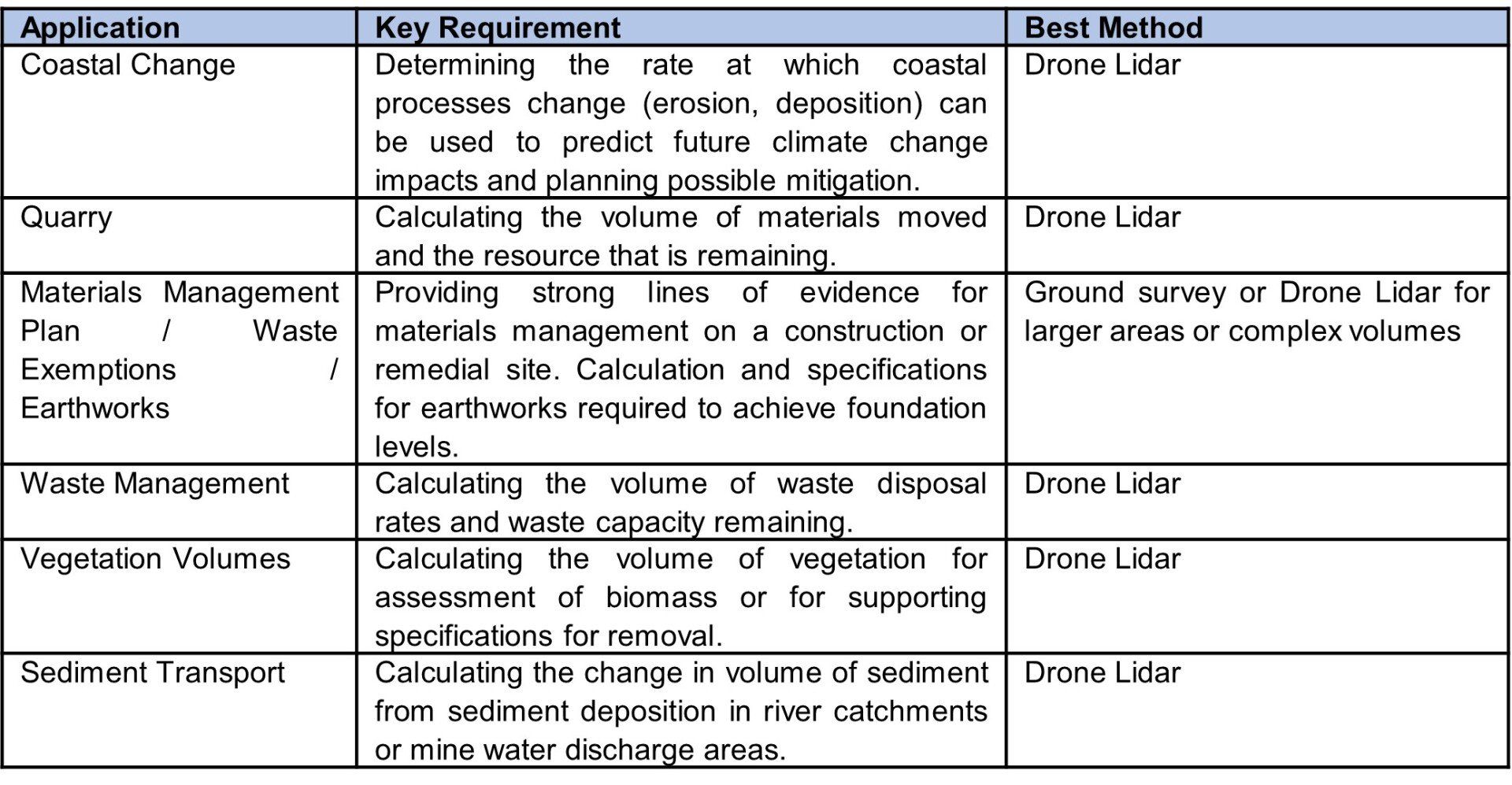
Use Case Applications
There are a range of land and land use changes where the landscape and its volume changes. The following are examples where drone survey could enhance existing ground-based survey techniques.
Key Considerations
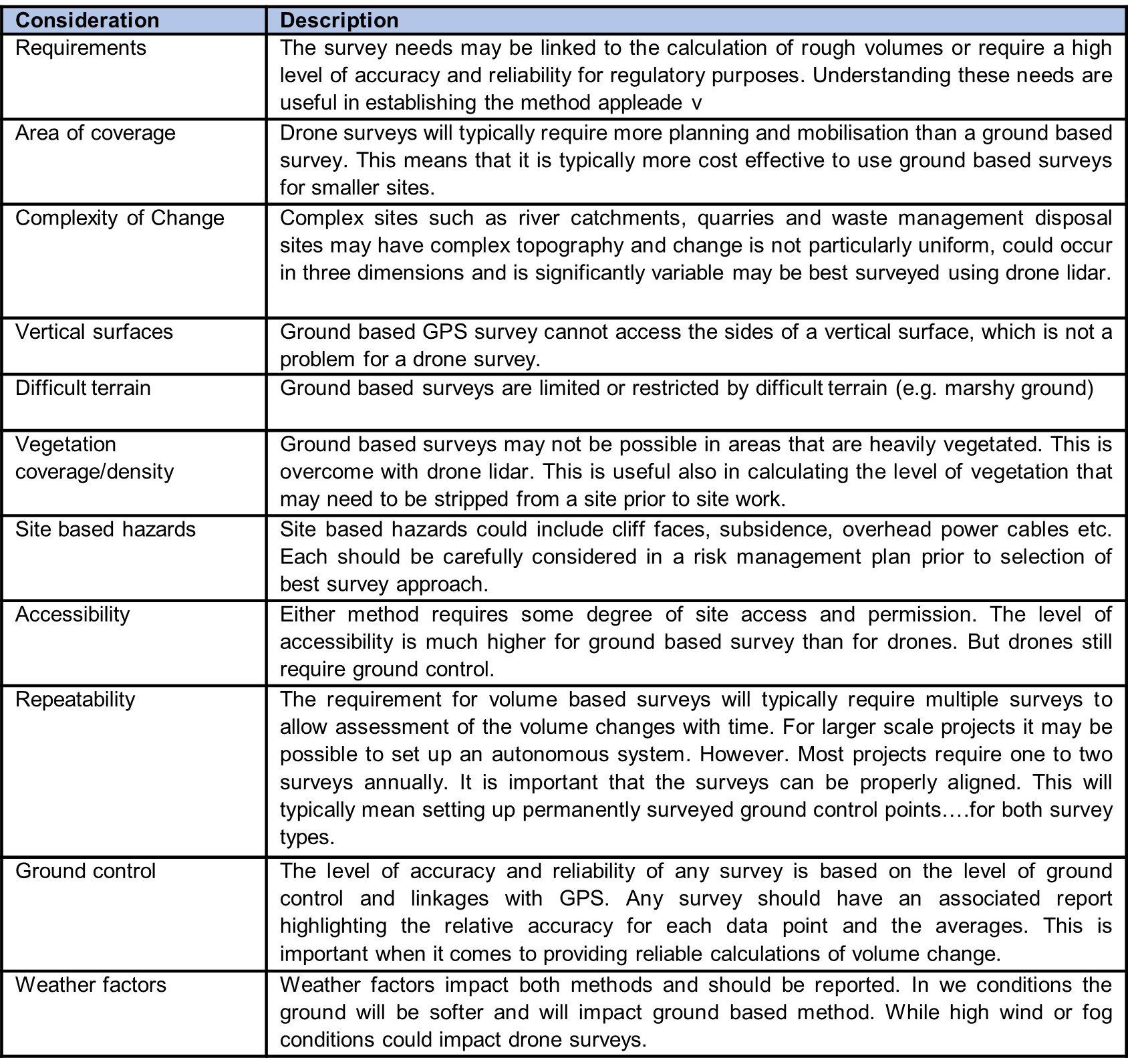
There are a range of considerations when considering a volumetric survey. The following summarises some of the main considerations in the method or process selected.
Construction Materials Management Plans
Construction materials management plans are typically required with earthwork and remedial projects where soils/waste/materials are moved on/off site or reused on site. Such plans are typically required with planning, remedial plans or waste management exemption plans to demonstrate changes to materials on site.
Traditional survey methods use ground based GPS station systems where points are surveyed at various intervals to support the development of a contour plan. This is useful and accurate for most MMPs and their compliance. However, for more complex sites (larger areas, more complex waste handling, planning purposes and area of uneven ground) a greater level of coverage is typically required. This can be achieved through drone based lidar and/or photogrammetry which can provide full coverage and where accurate volumes can be calculated quickly. The drones surveys can also be used to support monitoring of materials management within a site, the results used to support optimal materials management and regulatory compliance.
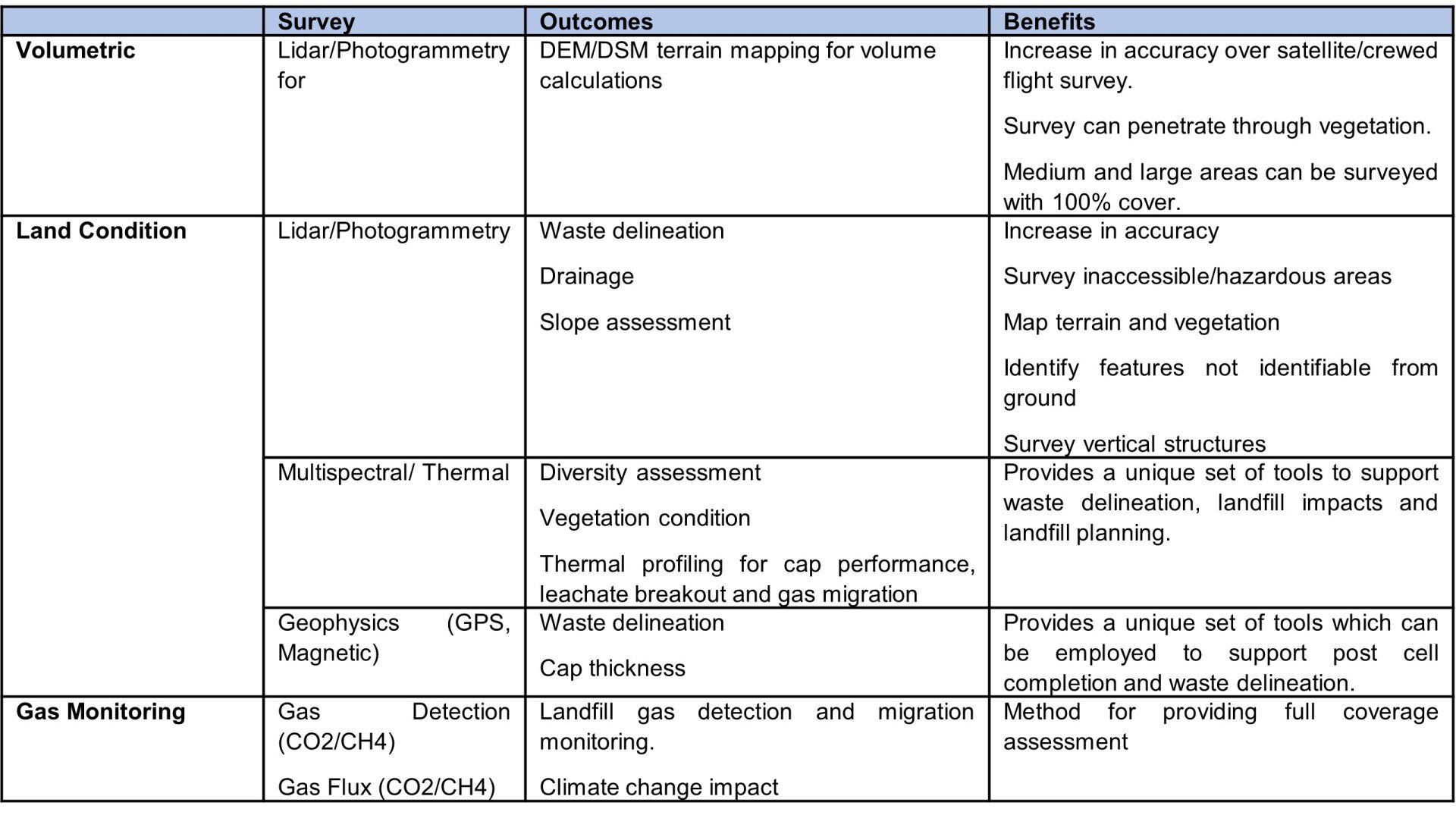
How can Drone Surveys Help
Drone survey platforms with sensors such as lidar, photogrammetry, multispectral, thermal, gas and geophysics can be used to provide greater survey coverage and provide insights that are not available from ground based survey, at a cost equivalent to ground based survey.
Surveying Examples
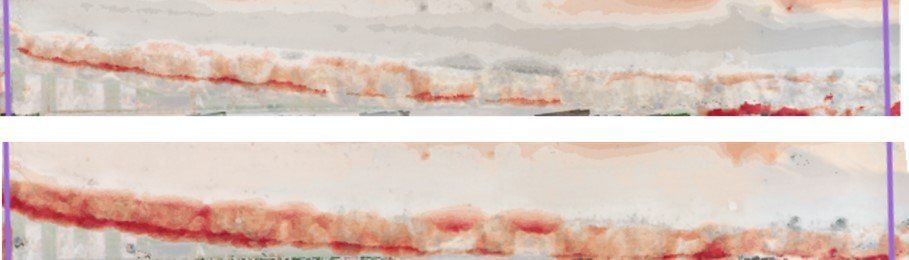
Survey of a coastal area on three occasions to determine volume change – image is a heat map of the changes. Data outcomes can provide accurate volumes relating to coastal erosion to support a coastal ‘balance sheet’ linked to areas of deposition in other areas of coast.
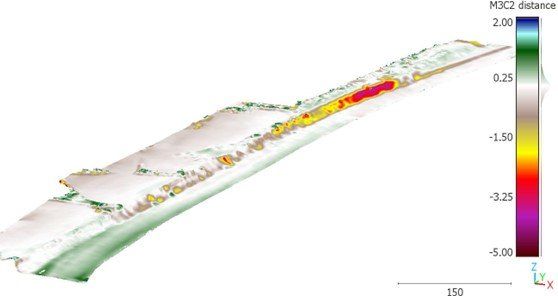
Survey of a coastal area to calculate rate of change of erosion processes in Suffolk.
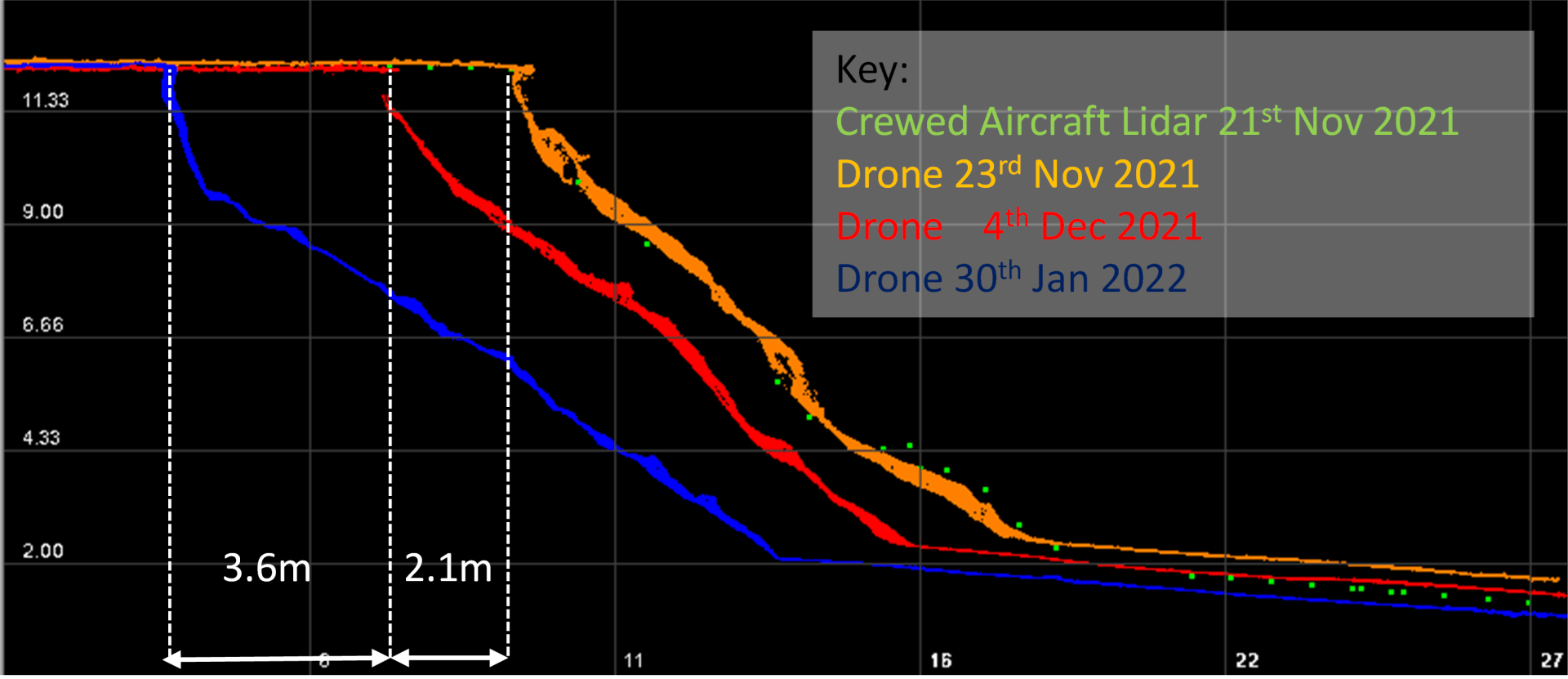
Survey of a coastal area with a cross section of change in vertical faces as a consequence of erosion. Sections can be generated for any part of the coastal area, along with volume changes.
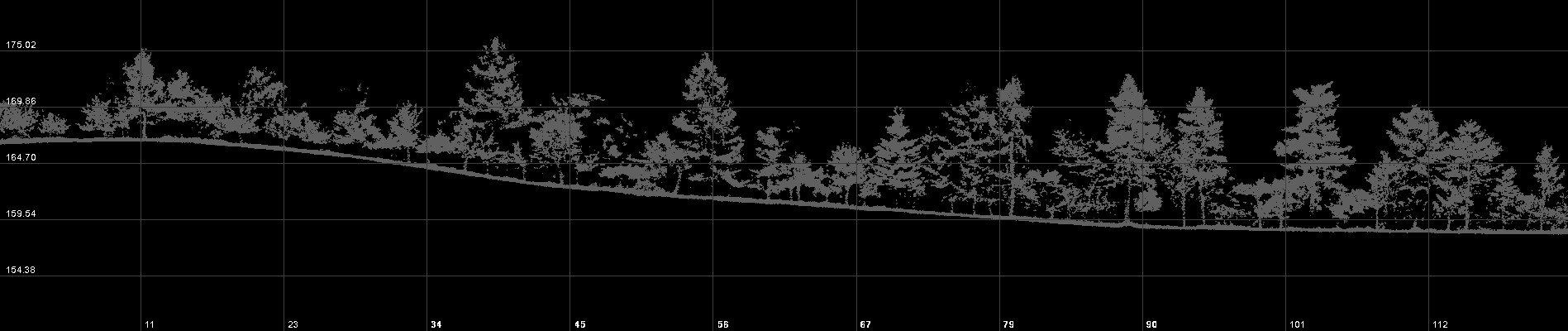
Cross section of a land survey within a highly vegetated area to derive terrain mapping and vegetation volumes.
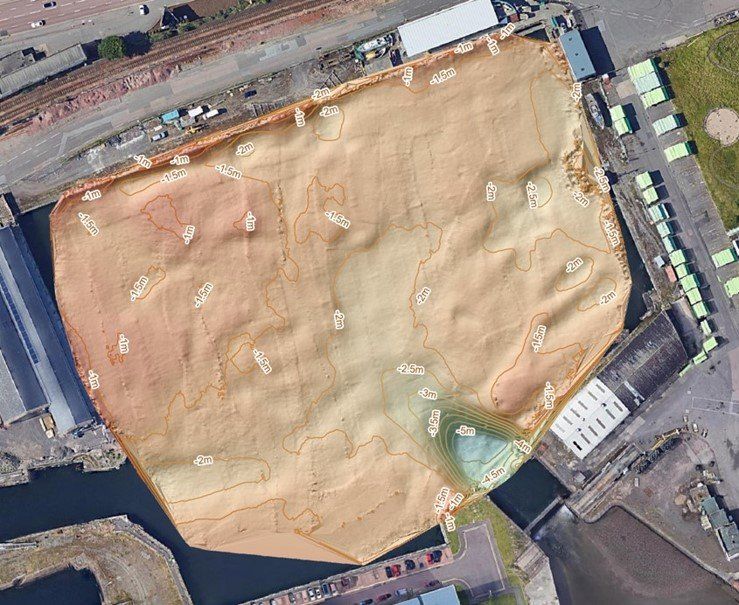

Example of a bathymetry survey used to support calculation of changes in sediment volumes within a dock area.
See Also
