BS13: Archaeological
Archaeological survey will use a triage approach of non-invasive survey techniques from satellite to crewed fixed wing and then land based. Drone surveys with specialised sensor technology offers an additional solution to support archaeologists with greater coverage, increased accuracy and richer data.
Definition
Archaeological surveys include examination of land for information about the location, distribution and organization of past human cultures. The process is typically managed by expert archaeologists who will have some learned knowledge of features and assets from past heritage that are important and which need to be recorded and/or preserved. Archaeological surveys tend to be triggered in the development planning process, particularly where there is a strong likelihood of the presence of possible artifacts.
An archaeological survey may include an assessment of the land condition, a dig and a detailed recording of the artifacts, assets or features. The process may continue in conjunction with a development project with further work and records being made under a watching brief.

How can Drone Surveys Help
Drones have the potential to reveal insights and features that cannot be gained from ground based activity. Minor changes in land topography or condition, often obscured through vegetation and trees, can show the outline or layout of historical activity, natural or man-made. Drones can provide the aerial platform to allow specialist sensor technologies to unlock some of our hidden past.
The following table highlights some of the survey technologies that can be deployed via a drone platform, which may support the identification of archaeological features, which can enhance as well as speed the archaeological process.

Survey Benefits, Issues and Considerations
The following re-iterates some of the common issues that surveyors are faced with and which should be considered when selecting an appropriate survey method.
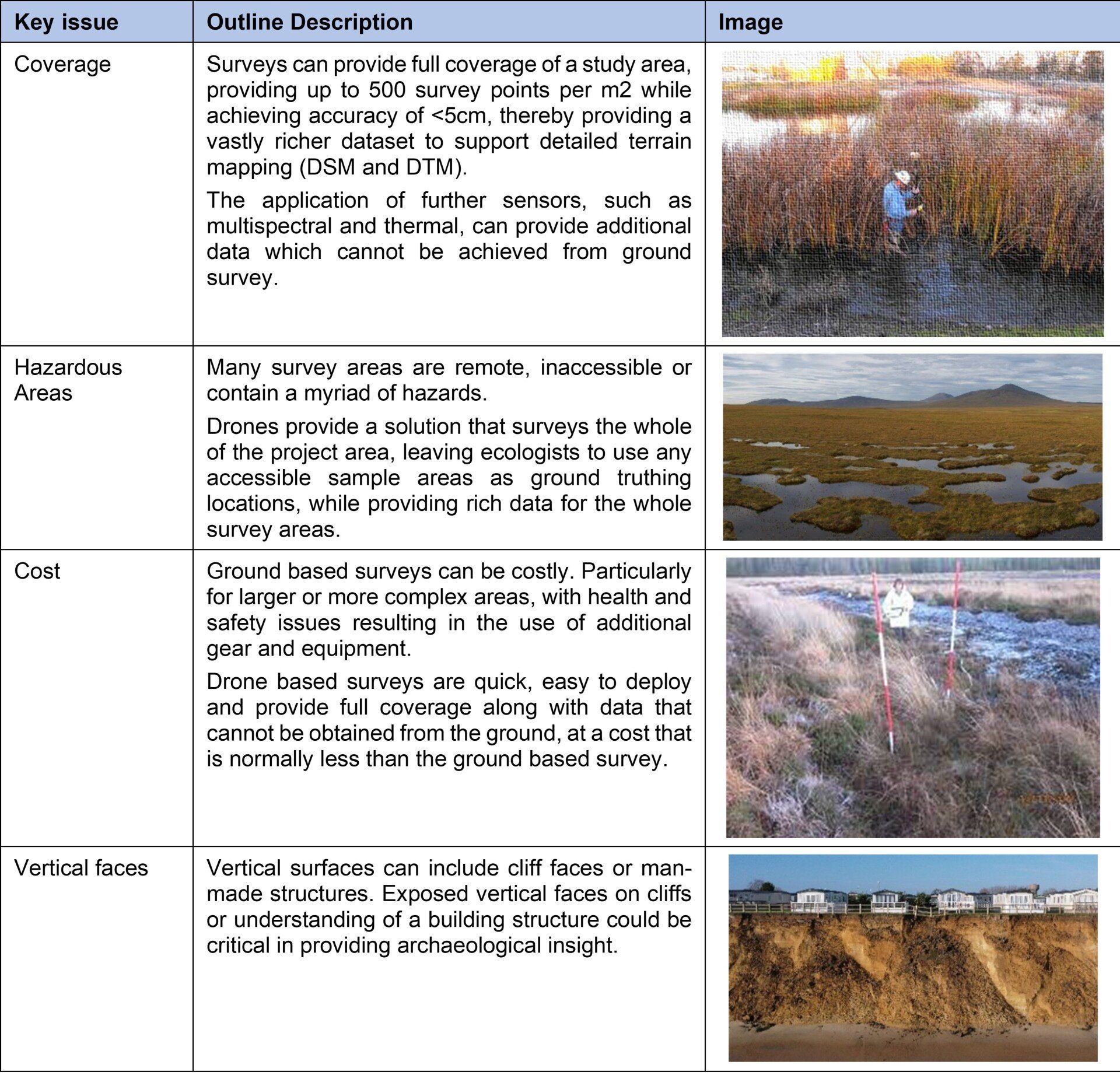
Drone based platforms are not infallible and have some limitations. These can include restricted flight areas and poor weather conditions. In many survey cases, it is useful to consider a number of survey tools from satellite data through to ground based survey. An aerial survey should not be a replacement for traditional ground based archaeological dig, but should be used to support and direct where best to dig.
Examples

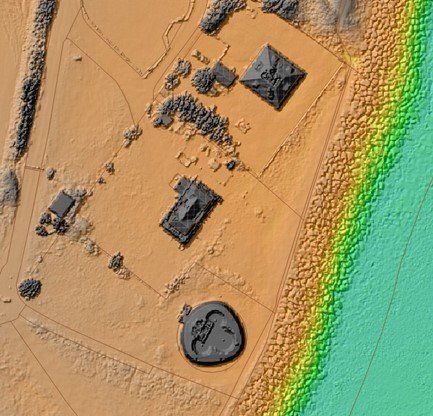
Example: Lidar survey of a coastal environment with areas of historical significance.
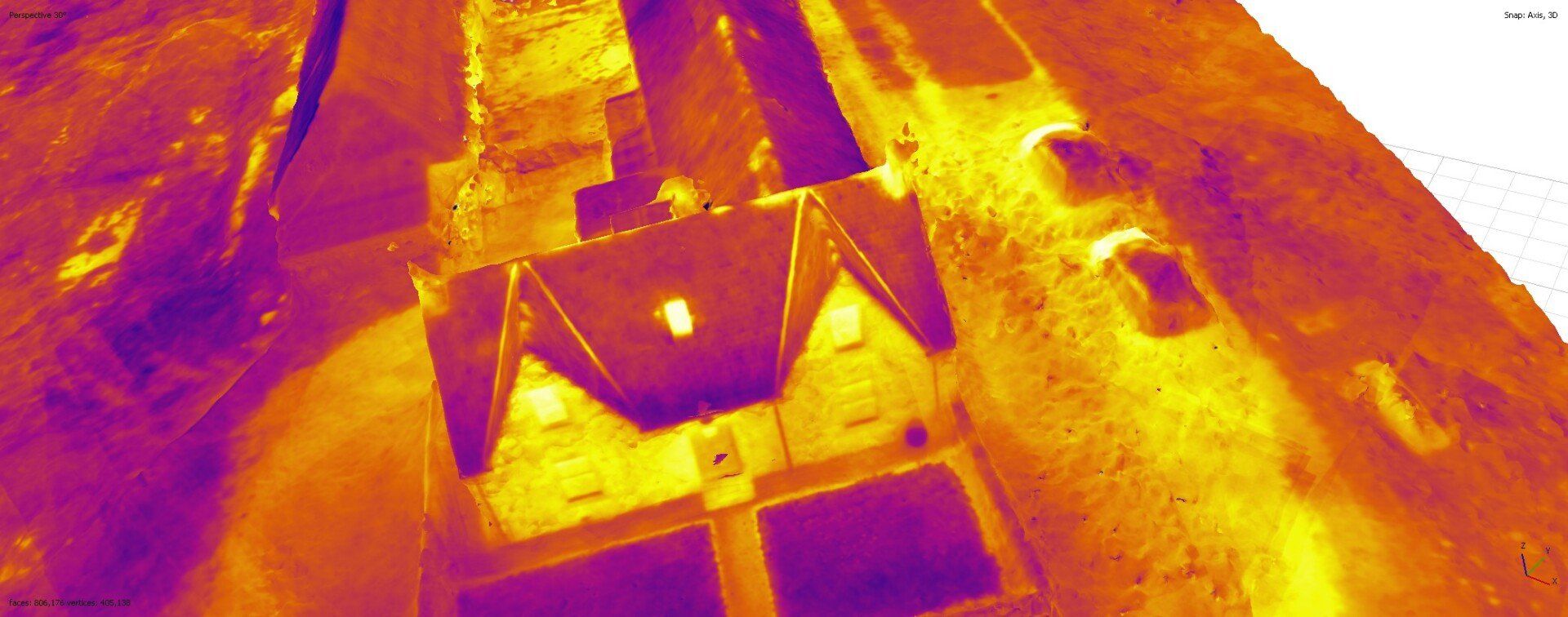

Example: Thermal imaging is a useful approach for assessment of near surface stone based structures.
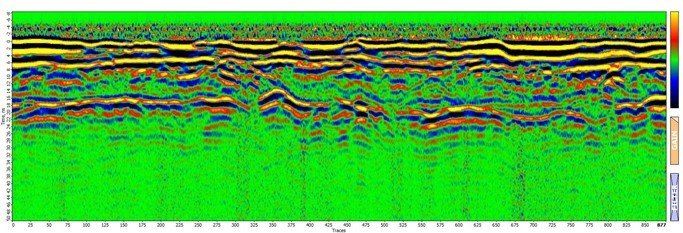
Example: Outcome section from a drone based ground probing radar survey

Example: Use of multispectral survey to support land based features on a site in the west of Scotland.
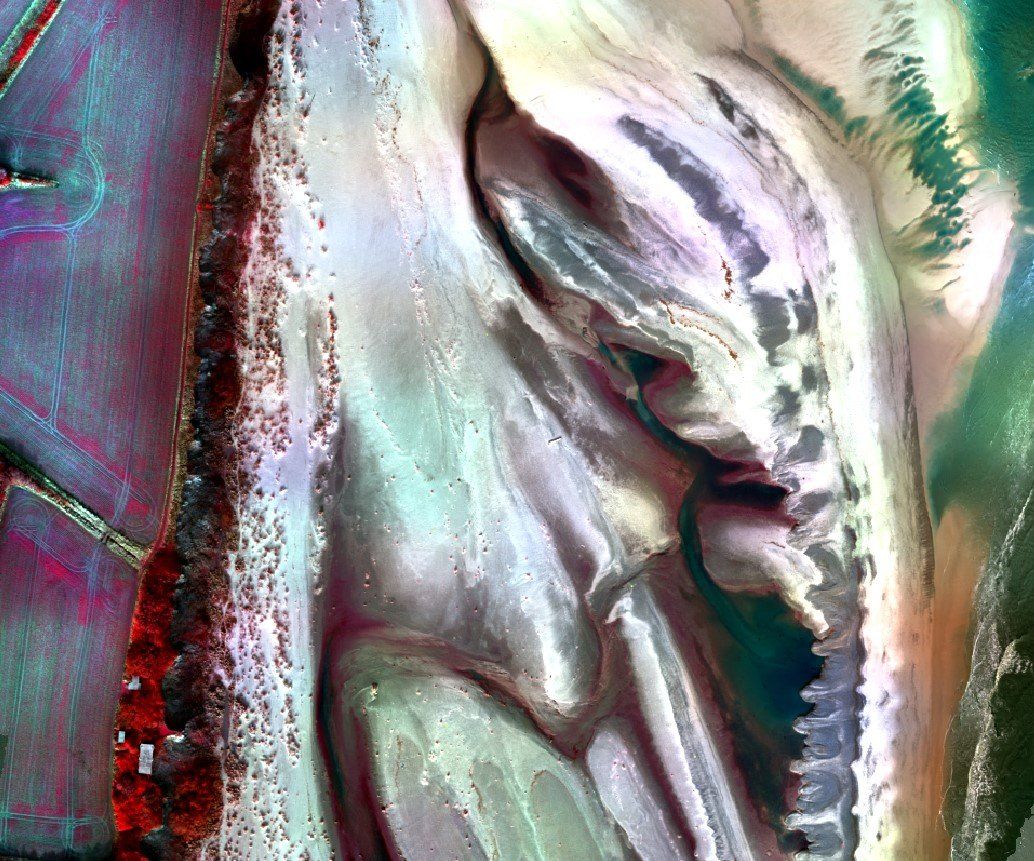

Example: Multispectral survey of coastal intertidal habitat using CIR for beach ness to assess to support identification of coastal structures.
See Also
